Find a counterexample to show that the statement is false. – Counterexamples play a crucial role in logic and mathematics, providing compelling evidence to refute false statements. By presenting specific instances that contradict a given statement, counterexamples expose its limitations and challenge its validity. This article delves into the significance of counterexamples, exploring their construction, implications, and applications in various fields.
Counterexamples serve as powerful tools for logical reasoning, enabling us to scrutinize the accuracy and validity of statements. They highlight the importance of critical thinking and the need to examine claims thoroughly before accepting them as true.
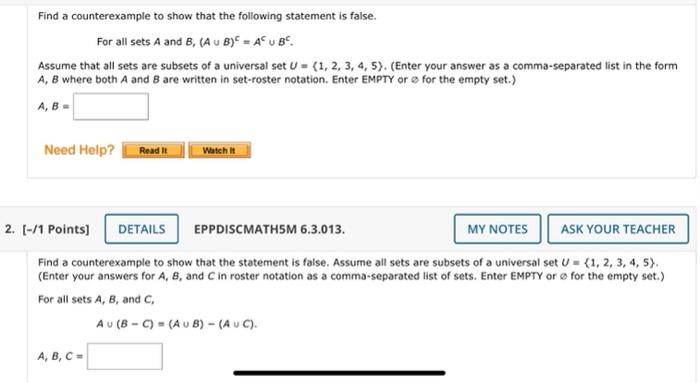
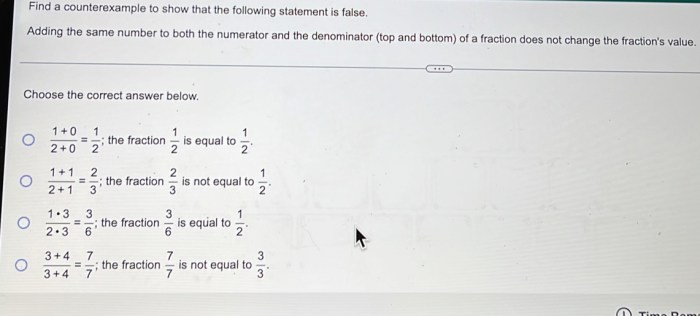
Statement Refutation: Find A Counterexample To Show That The Statement Is False.
To refute a statement, we provide a counterexample that contradicts its claim. A counterexample is a specific instance that demonstrates the statement’s falsity. By showing that there exists a situation where the statement does not hold true, we disprove its general validity.
The significance of a counterexample lies in its ability to challenge the statement’s underlying assumptions. It forces us to reconsider the statement’s logic and the conditions under which it might be true. Counterexamples play a crucial role in advancing scientific knowledge and critical thinking.
Counterargument Examples
Counterargument examples provide specific instances where a statement fails to hold true. These examples highlight the limitations of the statement and demonstrate that it does not apply universally. By identifying these exceptions, we can refine and improve the statement to make it more accurate and comprehensive.
The implications of counterargument examples are twofold. Firstly, they show that the statement is not universally true and should be treated with caution. Secondly, they provide valuable insights into the conditions under which the statement might be true or false, allowing us to develop a more nuanced understanding of the issue.
Logical Fallacies, Find a counterexample to show that the statement is false.
Logical fallacies are errors in reasoning that weaken the validity of a statement. By analyzing a statement for logical fallacies, we can identify its flaws and assess its credibility. Common logical fallacies include:
- Ad hominem: Attacking the person making the statement rather than the statement itself.
- Circular reasoning: Using the statement to prove itself.
- False dichotomy: Presenting only two options when more exist.
- Hasty generalization: Making a broad claim based on limited evidence.
Identifying logical fallacies helps us avoid being misled by flawed arguments and makes us more critical thinkers.
Alternative Perspectives
Exploring alternative perspectives challenges the assumptions underlying a statement. By considering different viewpoints, we can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the issue and identify potential biases or limitations in the original statement.
Alternative perspectives can come from different disciplines, cultures, or ideologies. They provide valuable insights into the complexities of the issue and help us develop a more balanced and nuanced perspective.
Historical Context
Examining the historical context in which a statement was made can shed light on its meaning and validity. Over time, the meaning of words and concepts can change, and the statement may no longer be applicable in the present context.
Understanding the historical context helps us avoid misinterpreting statements made in the past and appreciate the evolution of ideas and perspectives.
Quick FAQs
What is the purpose of a counterexample?
A counterexample is used to disprove a false statement by providing a specific instance that contradicts it.
How do counterexamples contribute to logical reasoning?
Counterexamples challenge the validity of statements, forcing us to re-examine their assumptions and refine our understanding.
What are some common types of logical fallacies that counterexamples can expose?
Counterexamples can reveal fallacies such as hasty generalization, circular reasoning, and false dilemma.