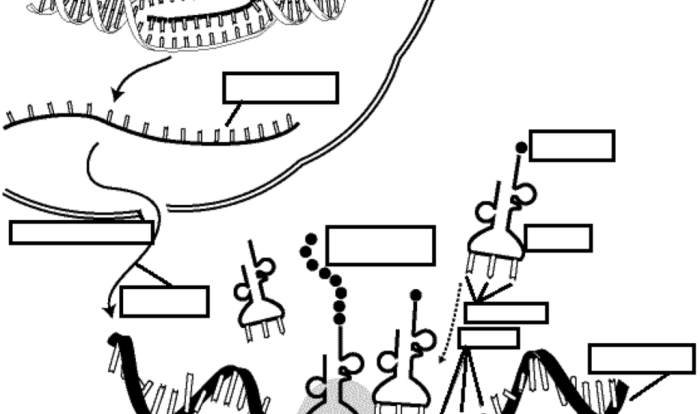
All of the following occur during RNA processing except: transcription, splicing, polyadenylation, and capping. These processes are essential for the maturation of RNA molecules and their subsequent roles in gene expression. Understanding the exceptions to these processes provides valuable insights into the regulation and diversity of RNA metabolism.
RNA Processing
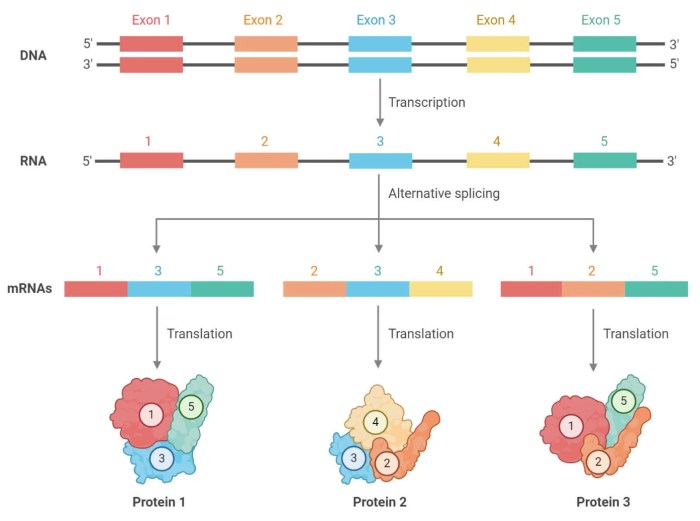
RNA processing is a series of modifications that occur to RNA molecules after they have been transcribed from DNA. These modifications include splicing, polyadenylation, and capping. RNA processing is essential for the proper function of RNA molecules in the cell.
Transcription
Transcription is the process of copying the genetic information from DNA into RNA. The enzyme RNA polymerase binds to the DNA and uses it as a template to synthesize a complementary RNA molecule. The RNA molecule is then released from the DNA and can be used to direct protein synthesis.
Molecules Involved in Transcription, All of the following occur during rna processing except:
* RNA polymerase: The enzyme that synthesizes RNA molecules.
DNA
The template for RNA synthesis.
Ribonucleotides
The building blocks of RNA molecules.
Splicing: All Of The Following Occur During Rna Processing Except:
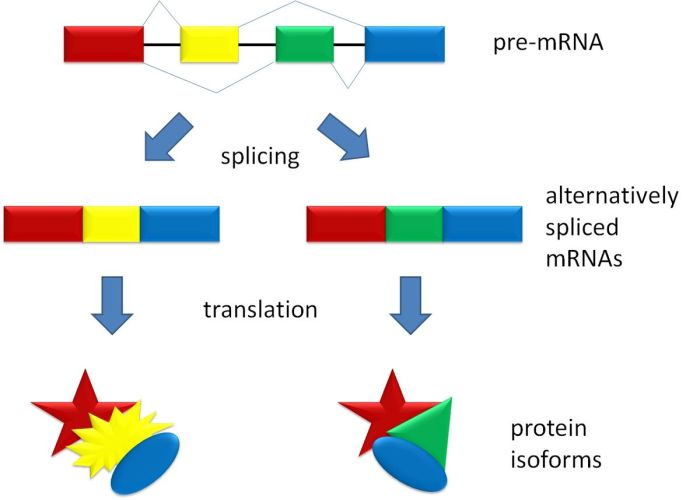
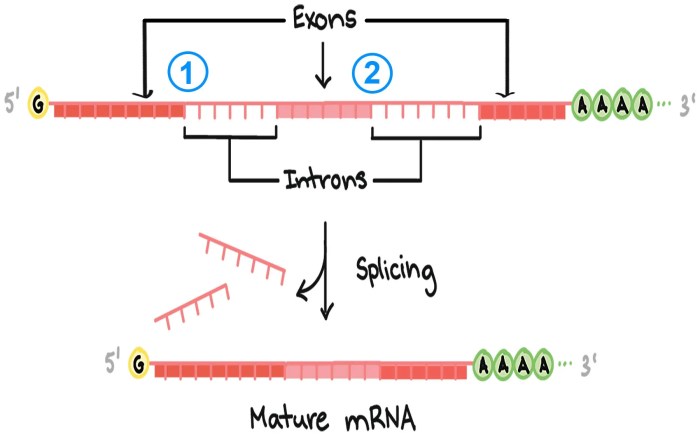
Splicing is the process of removing introns from RNA molecules. Introns are non-coding regions of RNA that are not necessary for protein synthesis. Exons are the coding regions of RNA that are translated into protein.
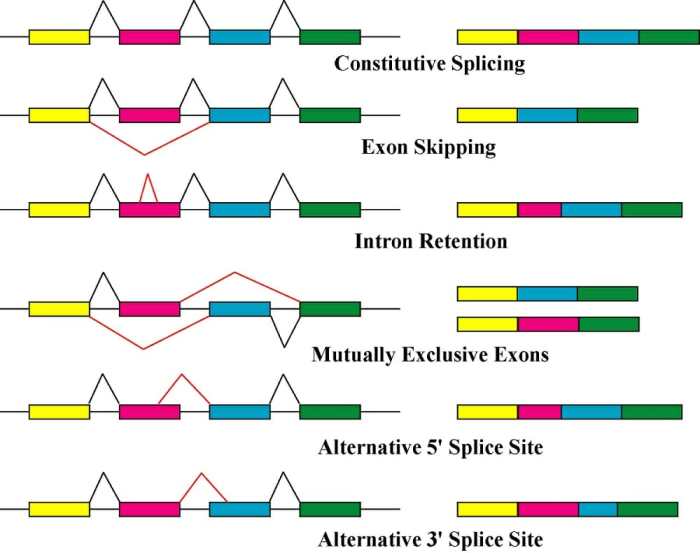
Types of RNA Splicing
* Constitutive splicing: The same introns are removed from all RNA molecules of a particular gene.
Alternative splicing
Different introns are removed from different RNA molecules of a particular gene, resulting in different protein products.
Polyadenylation
Polyadenylation is the process of adding a tail of adenine nucleotides to the 3′ end of RNA molecules. Polyadenylation increases the stability of RNA molecules and helps them to be translated into protein.
Capping
Capping is the process of adding a guanine nucleotide to the 5′ end of RNA molecules. Capping protects RNA molecules from degradation and helps them to be translated into protein.
Commonly Asked Questions
What is the main purpose of RNA processing?
RNA processing ensures the stability, functionality, and diversity of RNA molecules, enabling their roles in gene expression and cellular processes.
Can RNA processing occur in the cytoplasm?
While most RNA processing steps occur in the nucleus, certain modifications, such as polyadenylation, can take place in the cytoplasm.