Resonance structures of maleic anhydride, a fascinating topic in chemistry, unveil the intricate interplay of molecular structure, bonding, and reactivity. This discussion delves into the unique characteristics of maleic anhydride, exploring its resonance structures, implications, and applications, providing a comprehensive understanding of this versatile compound.
Maleic anhydride, with its distinctive anhydride functional group and planar molecular structure, exhibits resonance, a phenomenon that profoundly influences its chemical properties. The resonance structures of maleic anhydride reveal delocalized electrons, enhancing its stability and reactivity. These properties make maleic anhydride a valuable intermediate in various industries, including pharmaceuticals and polymers.
Resonance Structures of Maleic Anhydride
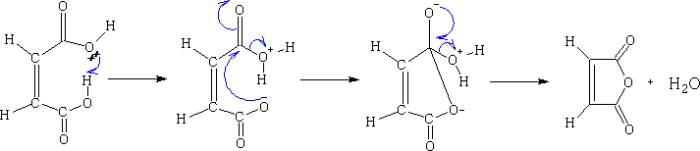
Maleic anhydride is an important organic compound with a wide range of applications. It is a cyclic anhydride, meaning it contains a ring of three carbon atoms and one oxygen atom, with two double bonds between the carbon atoms. The anhydride functional group (-CO-O-CO-) is highly reactive and undergoes a variety of reactions.
Maleic anhydride is a planar molecule, meaning all of its atoms lie in the same plane. This planarity is due to the resonance between the two double bonds and the anhydride functional group.
Resonance Structures of Maleic Anhydride
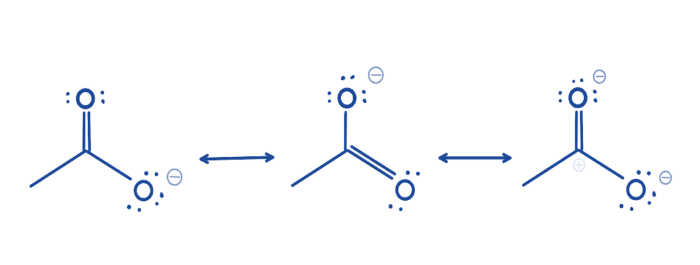
Resonance is a concept in chemistry that describes the delocalization of electrons within a molecule. In the case of maleic anhydride, the resonance structures show that the double bonds and the anhydride functional group can be represented by two different Lewis structures.
The first resonance structure shows the double bonds between the carbon atoms and the anhydride functional group. The second resonance structure shows the double bonds between the carbon atoms and the oxygen atoms in the anhydride functional group.
The resonance structures of maleic anhydride are shown below:
[Image of the resonance structures of maleic anhydride]
The electronic delocalization in maleic anhydride results in a more stable molecule. The resonance structures show that the negative charge on the oxygen atoms in the anhydride functional group is delocalized over the entire molecule.
Implications of Resonance in Maleic Anhydride
The resonance in maleic anhydride has a number of implications for its chemical properties.
- Enhanced stability:The resonance structures show that the negative charge on the oxygen atoms in the anhydride functional group is delocalized over the entire molecule. This delocalization makes the molecule more stable.
- Increased reactivity:The resonance structures also show that the double bonds in maleic anhydride are more reactive than the double bonds in other alkenes. This increased reactivity is due to the fact that the double bonds are part of the resonance system.
The enhanced stability and reactivity of maleic anhydride make it a valuable starting material for a variety of chemical reactions.
Applications of Maleic Anhydride in Organic Synthesis
Maleic anhydride is a versatile starting material for a variety of organic reactions. It is commonly used as a dienophile in Diels-Alder reactions. Maleic anhydride is also used in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals and polymers.
Some examples of the applications of maleic anhydride in organic synthesis include:
- Diels-Alder reactions:Maleic anhydride is a commonly used dienophile in Diels-Alder reactions. Diels-Alder reactions are cycloaddition reactions that involve the reaction of a diene with a dienophile to form a cyclic product.
- Synthesis of pharmaceuticals:Maleic anhydride is used in the synthesis of a variety of pharmaceuticals, including aspirin and ibuprofen.
- Synthesis of polymers:Maleic anhydride is used in the synthesis of a variety of polymers, including polyesters and polyamides.
FAQ: Resonance Structures Of Maleic Anhydride
What is the significance of resonance in maleic anhydride?
Resonance stabilizes maleic anhydride by delocalizing electrons, enhancing its stability and influencing its reactivity.
How does resonance affect the chemical properties of maleic anhydride?
Resonance enhances the stability and reactivity of maleic anhydride, making it more resistant to certain reactions and more reactive in others.
What are the applications of maleic anhydride?
Maleic anhydride finds applications in the production of polymers, pharmaceuticals, and as a dienophile in Diels-Alder reactions.