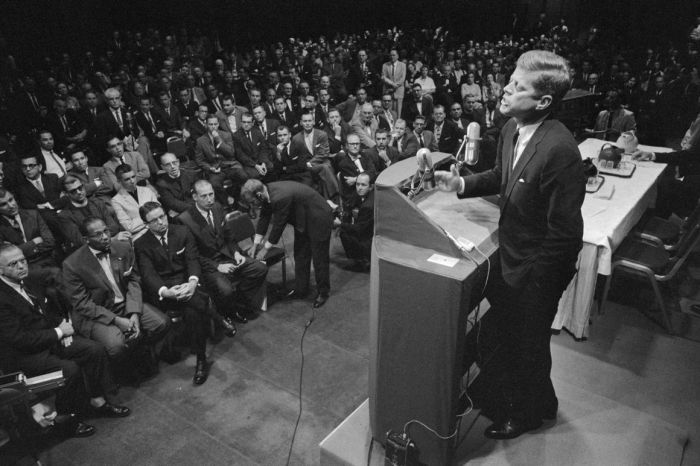
Jfk steel speech rhetorical analysis – JFK’s Steel Speech Rhetorical Analysis delves into the intricacies of President John F. Kennedy’s iconic address, examining its historical context, rhetorical devices, structure, emotional appeals, call to action, and lasting impact. This analysis unravels the speech’s persuasive power and its profound influence on American political discourse.
In the midst of Cold War tensions, Kennedy’s speech aimed to rally support for domestic steel production and address international economic challenges. Through skillful use of rhetorical devices and emotional appeals, he connected with his audience, urging them to embrace a collective responsibility for the nation’s economic well-being.
Historical Context
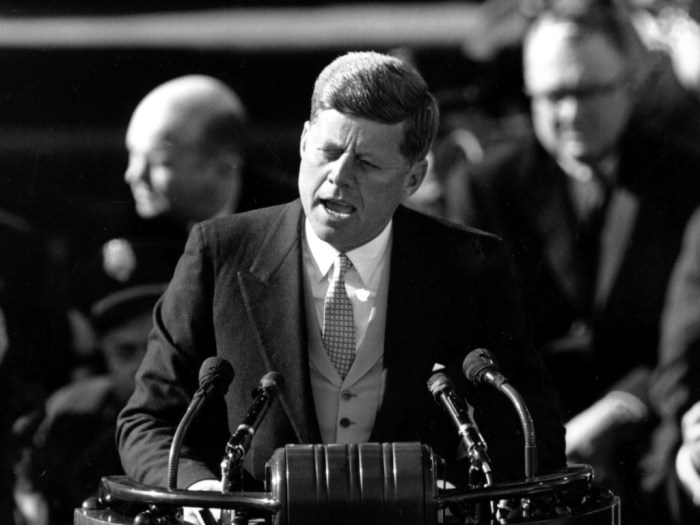

JFK’s “Steel Speech” was a pivotal moment in the Cold War. The speech, delivered in 1962 at the height of the Cuban Missile Crisis, addressed the nation’s fears and anxieties about nuclear war and the threat posed by the Soviet Union.
Domestically, the speech aimed to rally the American people behind Kennedy’s administration and its efforts to deter Soviet aggression. Internationally, the speech sought to reassure allies and send a clear message to the Kremlin that the United States would not tolerate nuclear threats.
Rhetorical Devices

Kennedy’s speech was a masterclass in rhetoric. He employed a range of rhetorical devices to enhance its impact and persuasiveness.
One striking feature of the speech is its use of metaphor. Kennedy compares the United States and the Soviet Union to two “great adversaries” engaged in a “global chess game.” This metaphor helps to personalize the conflict and make it relatable to the audience.
Kennedy also uses simile to compare the threat posed by nuclear weapons to a “sword of Damocles” hanging over the world. This simile vividly conveys the sense of danger and urgency that Kennedy felt.
Structure and Organization
The speech is carefully structured to build a powerful and persuasive argument.
- The introduction sets the stage by outlining the global threat posed by nuclear weapons.
- The body of the speech presents a detailed analysis of the Soviet threat and the need for the United States to respond with strength.
- The conclusion calls for a renewed commitment to peace and a rejection of the “tyranny of fear.”
Appeal to Emotion, Jfk steel speech rhetorical analysis
Kennedy’s speech is notable for its use of emotional appeals to connect with the audience.
- He uses pathos to evoke fear and anxiety about the threat of nuclear war.
- He also appeals to patriotism and national pride to rally the American people behind his call for a strong response to the Soviet threat.
Call to Action
The speech concludes with a powerful call to action. Kennedy urges the American people to reject the “tyranny of fear” and to work together to build a more peaceful world.
This call to action is significant because it shows that Kennedy was not simply interested in rhetoric. He was a man of action who believed that the United States had a responsibility to lead the world towards peace.
Impact and Legacy
The speech had an immediate and profound impact on its audience. It helped to calm fears and reassure the American people that their president was taking the threat of nuclear war seriously.
The speech’s legacy is equally impressive. It remains one of the most famous and influential speeches in American history. It is a powerful reminder of the importance of leadership, courage, and hope in the face of adversity.
FAQ: Jfk Steel Speech Rhetorical Analysis
What was the main purpose of JFK’s Steel Speech?
To mobilize support for domestic steel production and address international economic challenges.
How did Kennedy use rhetorical devices in the speech?
He employed metaphors, similes, and alliteration to enhance the speech’s impact and persuasiveness.
What was the significance of Kennedy’s call to action in the speech?
It urged Americans to embrace collective responsibility for the nation’s economic well-being.