Learning through art arthropod anatomy emerges as a captivating and innovative approach to comprehending the intricate complexities of the animal kingdom’s most diverse phylum. This novel educational method harnesses the power of artistic expression to illuminate the remarkable structural adaptations and anatomical intricacies of arthropods, fostering a deeper appreciation for their evolutionary significance and ecological roles.
Through artistic representations, we gain a profound understanding of arthropod anatomy, transcending the limitations of traditional textbooks and unlocking a realm of visual exploration. Anatomical illustrations, sculptures, and models serve as vivid teaching tools, enabling students to visualize and interact with the subject matter in a tangible and engaging manner.
1. Introduction to Arthropod Anatomy
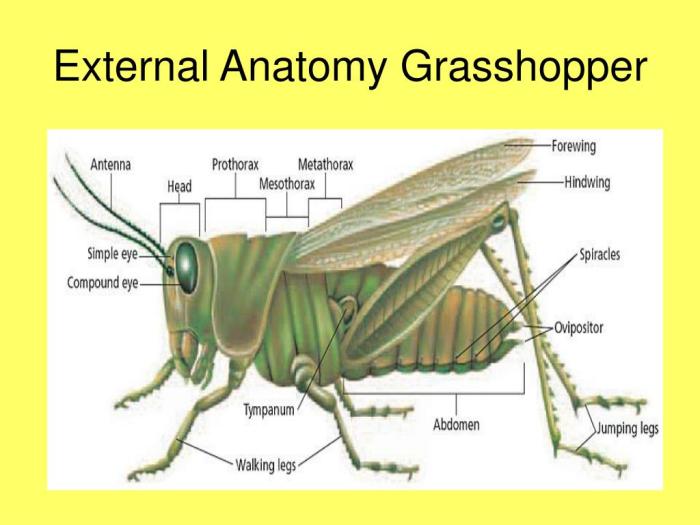
Arthropods, the largest phylum in the animal kingdom, exhibit an astounding diversity of forms and functions. Their unique body structure, characterized by segmented bodies, jointed appendages, and a hard exoskeleton, has allowed them to thrive in a wide range of habitats.
Understanding arthropod anatomy is essential for unraveling the secrets of their evolutionary success and ecological importance. This section provides an overview of arthropod body structure, highlighting key features and variations among different groups.
Arthropod Body Structure
Arthropods share a common body plan consisting of three main regions: the head, thorax, and abdomen. The head bears sensory organs, mouthparts, and the brain. The thorax is composed of segments bearing jointed appendages, typically including legs, wings, or both.
The abdomen contains digestive, reproductive, and excretory organs.
Unique Features of Arthropods
- Segmented Body:Arthropods’ bodies are divided into a series of segments, each with its own set of muscles and nerves.
- Jointed Appendages:Their limbs are jointed, allowing for a wide range of movements and adaptations.
- Hard Exoskeleton:The external skeleton, made of chitin, provides protection and support.
- Open Circulatory System:Blood flows freely within the body cavity, rather than through closed vessels.
Arthropod Diversity
Arthropods encompass a vast array of groups, including insects, crustaceans, arachnids, and myriapods. Each group exhibits unique anatomical variations that reflect their specialized adaptations. For instance, insects have six legs, while crustaceans have ten.
2. Learning Anatomy through Art
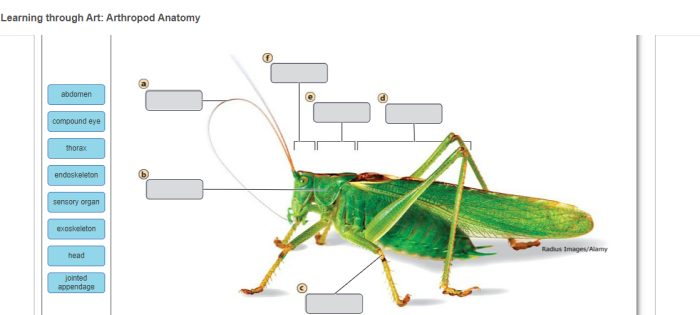
Art, in its various forms, has long been recognized as a powerful tool for enhancing learning and understanding. This section explores the benefits of using art as a means to teach and learn arthropod anatomy.
Benefits of Artistic Representations
- Enhanced Visualization:Artistic representations provide visual aids that help students visualize complex anatomical structures.
- Improved Comprehension:By translating anatomical concepts into visual form, art can make them more accessible and understandable.
- Stimulated Imagination:Artistic interpretations encourage students to engage their imaginations and explore different perspectives on anatomy.
Examples of Anatomical Art, Learning through art arthropod anatomy
Numerous examples showcase the effectiveness of art in conveying arthropod anatomy. Leonardo da Vinci’s sketches, for instance, captured the intricate details of insect wings and joints. Modern anatomical illustrations, such as those by Eleanor Lutz, employ precise lines and vibrant colors to depict arthropod structures.
3. Art-Based Activities for Learning
Incorporating art-based activities into the study of arthropod anatomy can enhance student engagement and deepen their understanding. This section presents practical ideas for art-based activities.
Drawing and Sketching
Students can create detailed drawings or sketches of arthropod specimens or anatomical models. This activity encourages close observation and helps them identify and label different body parts.
Model Building
Building models or sculptures of arthropods can provide a hands-on experience of their anatomy. Students can use various materials, such as clay, paper-mâché, or Lego, to represent the different body segments and appendages.
Lesson Plan Integration
Art-based activities can be seamlessly integrated into anatomy curricula. For instance, a lesson on insect morphology could include a drawing exercise where students sketch the different types of wings and antennae.
4. Artistic Interpretation of Arthropod Anatomy
Beyond its educational value, art also plays a significant role in interpreting and representing arthropod anatomy. This section discusses the interplay between imagination and creativity in depicting arthropods.
Role of Imagination
Artists often use their imaginations to enhance the visual appeal of their arthropod representations. They may exaggerate certain features or add decorative elements to create visually striking images.
Artistic Interpretations
Artistic interpretations of arthropods vary widely, reflecting the unique perspectives and styles of different artists. Some artists depict arthropods with a focus on scientific accuracy, while others emphasize their beauty or symbolic significance.
Examples of Artistic Representations
Examples of artistic interpretations of arthropods include the surrealist paintings of Salvador Dalí, the hyperrealistic sculptures of Duane Hanson, and the whimsical illustrations of Maurice Sendak.
5. Integrating Art into Education: Learning Through Art Arthropod Anatomy
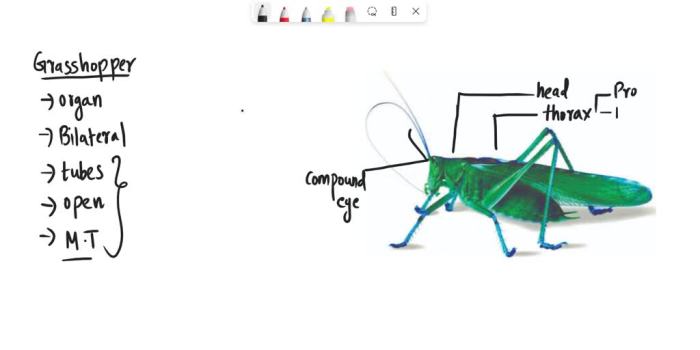
Art-based activities offer numerous benefits for anatomy education. This section provides recommendations for incorporating art into the classroom.
Incorporating Art Activities
Art-based activities can be integrated into anatomy curricula at various levels. Simple drawing exercises can be used as introductory activities, while more complex projects, such as model building, can be incorporated into larger units.
Fostering Student Engagement
Art-based activities can increase student engagement and motivation. By providing a creative outlet, art helps students connect with the material on a personal level.
Improving Learning Outcomes
Studies have shown that incorporating art into education can improve learning outcomes. Artistic representations can help students retain information and develop a deeper understanding of complex concepts.
Challenges and Opportunities
While integrating art into education offers many benefits, it also presents certain challenges. These include the need for time and resources, as well as the potential for students to focus more on artistic expression than on scientific accuracy.
FAQ Insights
What are the benefits of using art to learn arthropod anatomy?
Art provides a unique and engaging way to visualize and understand complex anatomical structures, enhancing memory and comprehension.
How can artistic representations improve the understanding of arthropod anatomy?
Artistic representations allow students to interact with the subject matter in a tangible and immersive way, facilitating a deeper understanding of anatomical relationships and adaptations.
What are some examples of art-based activities that can be used to teach arthropod anatomy?
Drawing or sketching body parts, creating models or sculptures, and designing lesson plans that incorporate artistic expression are effective art-based activities for teaching arthropod anatomy.
