Hesi case study premature infant – Navigating the HESI Case Study on Premature Infants: A Comprehensive Guide for Nurses. Dive into the complexities of caring for these fragile newborns, from assessment and planning to implementation and evaluation.
In this case study, we’ll explore the intricacies of providing optimal care for premature infants, emphasizing the crucial role of nurses in ensuring their well-being and development.
Introduction
A HESI Case Study Premature Infant is a simulated case study that presents a scenario involving a premature infant in a healthcare setting. It is designed to assess the knowledge, skills, and critical thinking abilities of healthcare students and professionals.
The purpose of a HESI Case Study is to provide a realistic and challenging environment for students to apply their learning and make decisions related to patient care. It helps them develop their clinical reasoning skills, problem-solving abilities, and ability to prioritize interventions.
Target Audience
HESI Case Study Premature Infant is primarily intended for healthcare students, including nursing, medical, and allied health students. It can also be used by healthcare professionals for continuing education and professional development.
Assessment
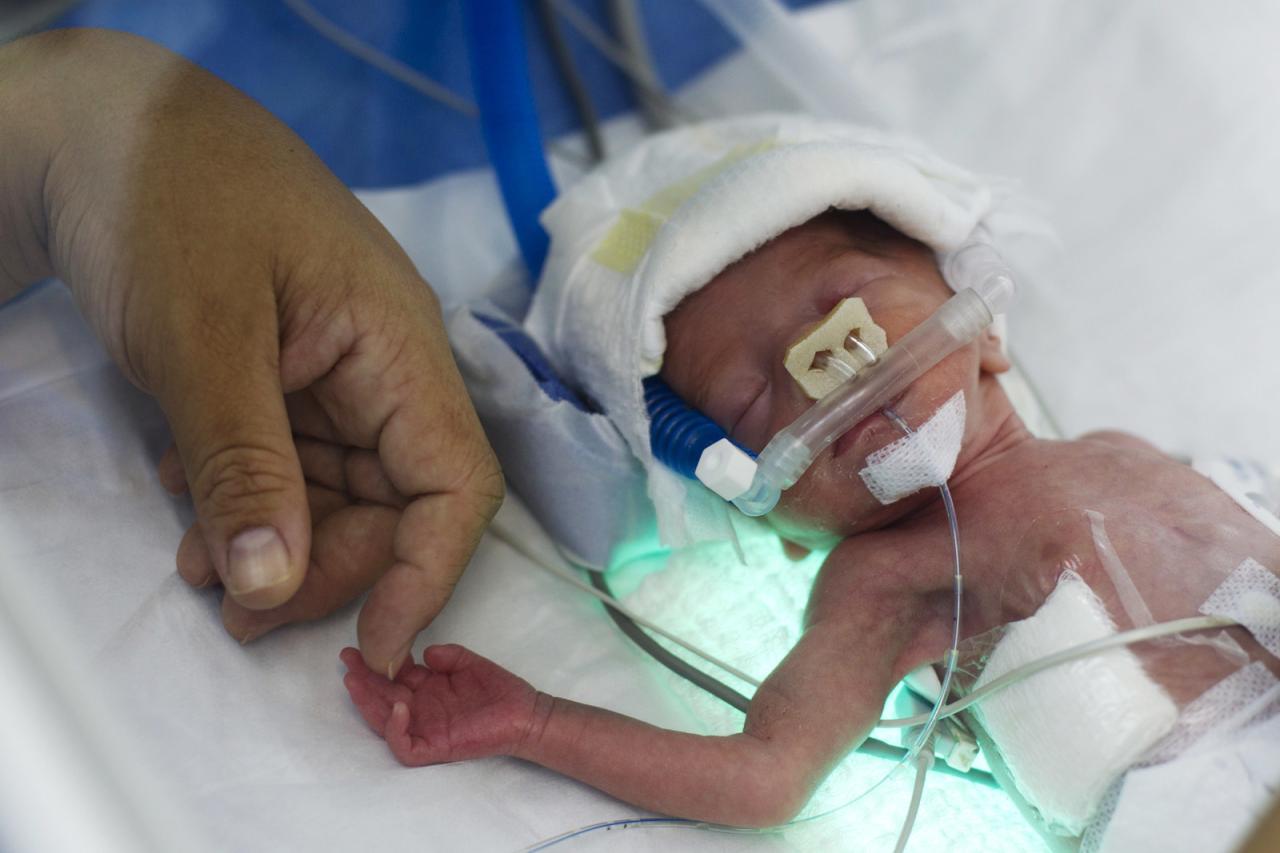
The assessment of a premature infant involves a comprehensive evaluation of the infant’s physical, developmental, and medical status. This assessment is crucial for identifying any potential health problems and ensuring appropriate care and interventions.
Nursing Interventions
- Maintaining a warm and humid environment to prevent hypothermia.
- Monitoring vital signs, including heart rate, respiratory rate, temperature, and oxygen saturation, to detect any abnormalities.
- Providing respiratory support, such as oxygen therapy or mechanical ventilation, if needed.
- Administering medications, such as antibiotics or surfactant, as prescribed by the healthcare provider.
- Promoting feeding through breast milk or formula, either orally or through a feeding tube.
- Providing skin care to prevent infections and promote healing.
Importance of Monitoring Vital Signs
Monitoring vital signs is essential for detecting any changes in the infant’s condition and intervening promptly. Abnormalities in vital signs can indicate underlying health problems, such as respiratory distress, sepsis, or hypoglycemia.
- Heart rate:Normal heart rate ranges from 120 to 160 beats per minute.
- Respiratory rate:Normal respiratory rate ranges from 30 to 60 breaths per minute.
- Temperature:Normal temperature ranges from 36.5 to 37.5 degrees Celsius.
- Oxygen saturation:Normal oxygen saturation ranges from 95% to 100%.
Role of Nutrition
Nutrition plays a vital role in the growth and development of a premature infant. Premature infants have increased nutritional needs due to their rapid growth rate and immature digestive system.
- Breast milk:Breast milk is the ideal nutrition for premature infants, as it contains all the essential nutrients and antibodies needed for growth and immunity.
- Formula:If breast milk is not available, premature infants can be fed with specially formulated infant formula that meets their nutritional needs.
- Feeding method:Premature infants may require feeding through a feeding tube until they are able to suck and swallow effectively.
Planning
Planning is a crucial aspect of providing comprehensive care for a premature infant. It involves developing a care plan that Artikels the infant’s needs, goals, and interventions. The care plan should be individualized to meet the specific requirements of the infant and should be regularly evaluated and updated as the infant’s condition changes.
The goals of the care plan should focus on promoting the infant’s growth, development, and well-being. These goals may include stabilizing the infant’s vital signs, providing adequate nutrition, preventing infections, and supporting the infant’s respiratory and neurological development.
Objectives of the Care Plan
- Establish and maintain a stable thermal environment.
- Provide adequate nutrition to support growth and development.
- Prevent and treat infections.
- Support respiratory function.
- Promote neurodevelopmental outcomes.
- Address the psychosocial needs of the infant and family.
Importance of Family Involvement
Family involvement is essential in the care of a premature infant. Families can provide emotional support, assist with feedings and diaper changes, and help to create a nurturing environment for the infant. They can also advocate for the infant’s needs and help to ensure that the care plan is followed.
Involving families in the care plan can improve the infant’s outcomes and help to reduce stress and anxiety for the family.
Implementation
Implementing appropriate nursing interventions is crucial for the well-being of premature infants. These interventions encompass a range of measures designed to address their specific needs and promote their optimal development.
Each intervention is meticulously chosen based on evidence-based practices and the infant’s individual condition. The rationale behind each intervention is to provide a nurturing environment that supports the infant’s growth and recovery.
Nursing Interventions
Nursing interventions for premature infants include:
- Maintaining a neutral thermal environment to prevent hypothermia or hyperthermia.
- Providing respiratory support, such as oxygen therapy or mechanical ventilation, to ensure adequate oxygenation.
- Administering intravenous fluids and electrolytes to maintain fluid balance and prevent dehydration.
- Monitoring vital signs, such as heart rate, respiratory rate, and temperature, to detect any abnormalities.
- Promoting skin-to-skin contact between the infant and parents to foster bonding and provide warmth.
- Administering medications, such as antibiotics or surfactants, as prescribed by the healthcare provider.
- Providing developmental care, such as gentle handling, positioning, and stimulation, to promote growth and prevent complications.
- Educating parents and caregivers about the infant’s condition and care needs.
li>Providing nutritional support through breast milk or formula, either through oral feeding or via a nasogastric tube.
Importance of Documentation
Accurate and comprehensive documentation is essential in the care of premature infants. It provides a detailed record of the infant’s condition, interventions implemented, and outcomes observed.
This documentation serves multiple purposes:
- Facilitates communication among healthcare providers, ensuring continuity of care.
- Tracks the infant’s progress over time, allowing for timely adjustments to the care plan.
- Provides a medico-legal record of the care provided.
- Supports research and quality improvement initiatives.
Evaluation
Evaluating the effectiveness of nursing interventions is crucial for optimizing patient outcomes and improving the quality of care. In the case of premature infants, ongoing assessment and evaluation are essential to ensure their well-being and developmental progress.
To evaluate the effectiveness of nursing interventions, it is important to consider both objective and subjective measures. Objective measures may include physiological parameters such as vital signs, weight gain, and growth charts. Subjective measures may include the infant’s behavior, feeding patterns, and response to stimuli.
Areas for Improvement in the Care Plan, Hesi case study premature infant
Based on the evaluation findings, areas for improvement in the care plan can be identified. This may involve adjusting the frequency or intensity of certain interventions, incorporating new strategies, or modifying the overall approach to care.
For example, if the infant is not gaining weight adequately, the nurse may need to increase the frequency of feedings or provide additional nutritional support. Alternatively, if the infant is exhibiting signs of stress or discomfort, the nurse may need to implement non-pharmacological pain management techniques.
Importance of Ongoing Evaluation
Ongoing evaluation is essential for ensuring that the care plan remains effective and responsive to the infant’s changing needs. As the infant grows and develops, their needs will evolve, and the nursing interventions must be adjusted accordingly.
Regular evaluation allows the nurse to identify any potential problems early on and intervene promptly to prevent complications. It also provides an opportunity to celebrate the infant’s progress and acknowledge the positive outcomes of the nursing care provided.
FAQ: Hesi Case Study Premature Infant
What is the purpose of a HESI Case Study?
HESI Case Studies provide a simulated clinical experience, allowing nursing students to apply their knowledge and critical thinking skills to real-world scenarios.
Why is monitoring vital signs crucial for premature infants?
Premature infants have immature organ systems, making them more susceptible to fluctuations in vital signs. Monitoring vital signs helps identify potential complications and intervene promptly.
How does nutrition play a role in the care of premature infants?
Premature infants have unique nutritional needs due to their rapid growth and development. Providing appropriate nutrition supports their overall well-being and reduces the risk of complications.